Description
Imports well-formed static HTML files into WordPress. Requires PHP 5.
This plugin will import a directory of files as either pages or posts. You may specify the HTML tag (e.g. <body>, <div id="content">, or <td width="732">) or Dreamweaver template region (e.g. ‹Main Content›) containing the content you want to import.
If importing pages, the directory hierarchy will be preserved. Directories containing the specified file types will be imported as empty parent pages (or, if an index file is present, its contents will be used for the parent page). Directories that do not contain the specified file types will be ignored.
As files are imported, the resulting IDs, permalinks, and titles will be displayed. On completion, the importer will provide a list of Apache redirects that can be used in your .htaccess file to seamlessly transfer visitors from the old file locations to the new WordPress permalinks. As of 2.0, if you change your permalink structure after you’ve imported your files, you can regenerate the redirects—the file’s old URL is stored as a custom field in the imported post.
Options:
- import files into any post type (posts, pages, or custom post types set to
public) - import linked media files (images, documents, etc.) to the media library
- select content, title, and custom fields by HTML tag or Dreamweaver template region
- remove a common phrase (such as the site name) from imported titles
- remove the imported title from within the content area
- upload a single file or scan a directory for files to import
- specify file extensions to import (e.g. html, htm, php)
- specify directories to exclude (e.g. images, css)
- if importing pages (or any hierarchical post type), specify whether your top-level files should become top-level pages or children of an existing page
- specify index file names (e.g. index.html, default.htm) whose contents should be used for the directory parent pages
- set tags, categories, and custom taxonomies
- choose status, author, and timestamp
- use meta descriptions as excerpts
- clean up imported HTML and strip unwanted tags and attributes in content and custom fields
- fix internal links in imported files to match new permalinks
- import the entire file and generate the title from the filename
- preserve the original filename as the imported page’s slug
- choose the date from an HTML tag or Dreamweaver region (uses strtotime(); results may vary)
- import additional HTML tags or Dreamweaver regions as custom fields
- option to remove imported title from within content area
- fallbacks: if your chosen tag/area is empty or does not exist, the importer will select
<body>for content and<title>for the title - use a custom field named ‹post_tag› to import tags from a portion of the file
See the User Guide for details on all the options.
Thanks
Thanks to…
- Tom Dyson’s Wordoff.org for inspiring the Word cleanup option in 1.1.
- Dion Hulse’s Add from Server plugin and bbqiguana’s Add Linked Images To Gallery plugin, from which I borrowed a lot of the logic behind the image import feature in 2.0
Screenshots
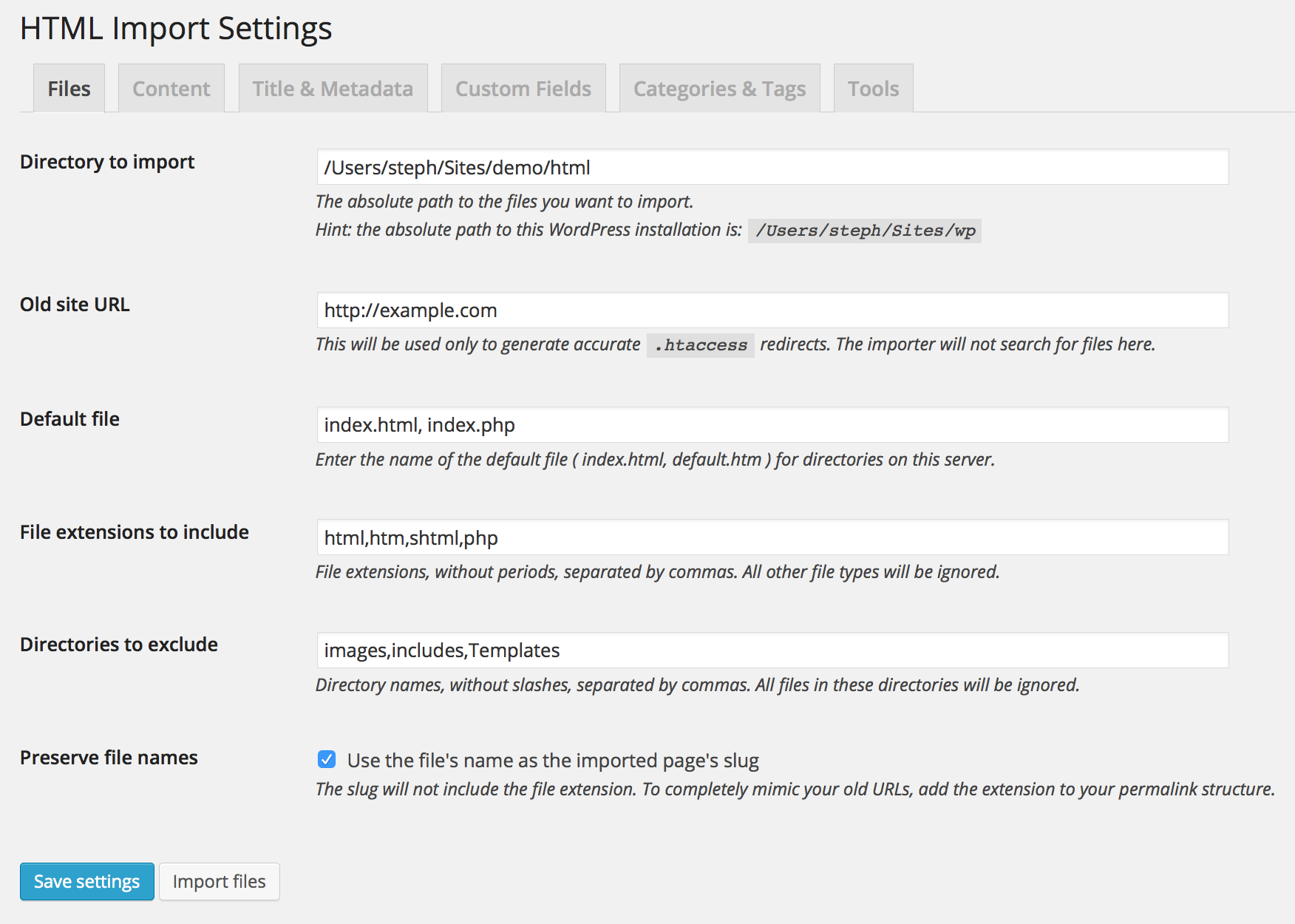
Settings for files to import 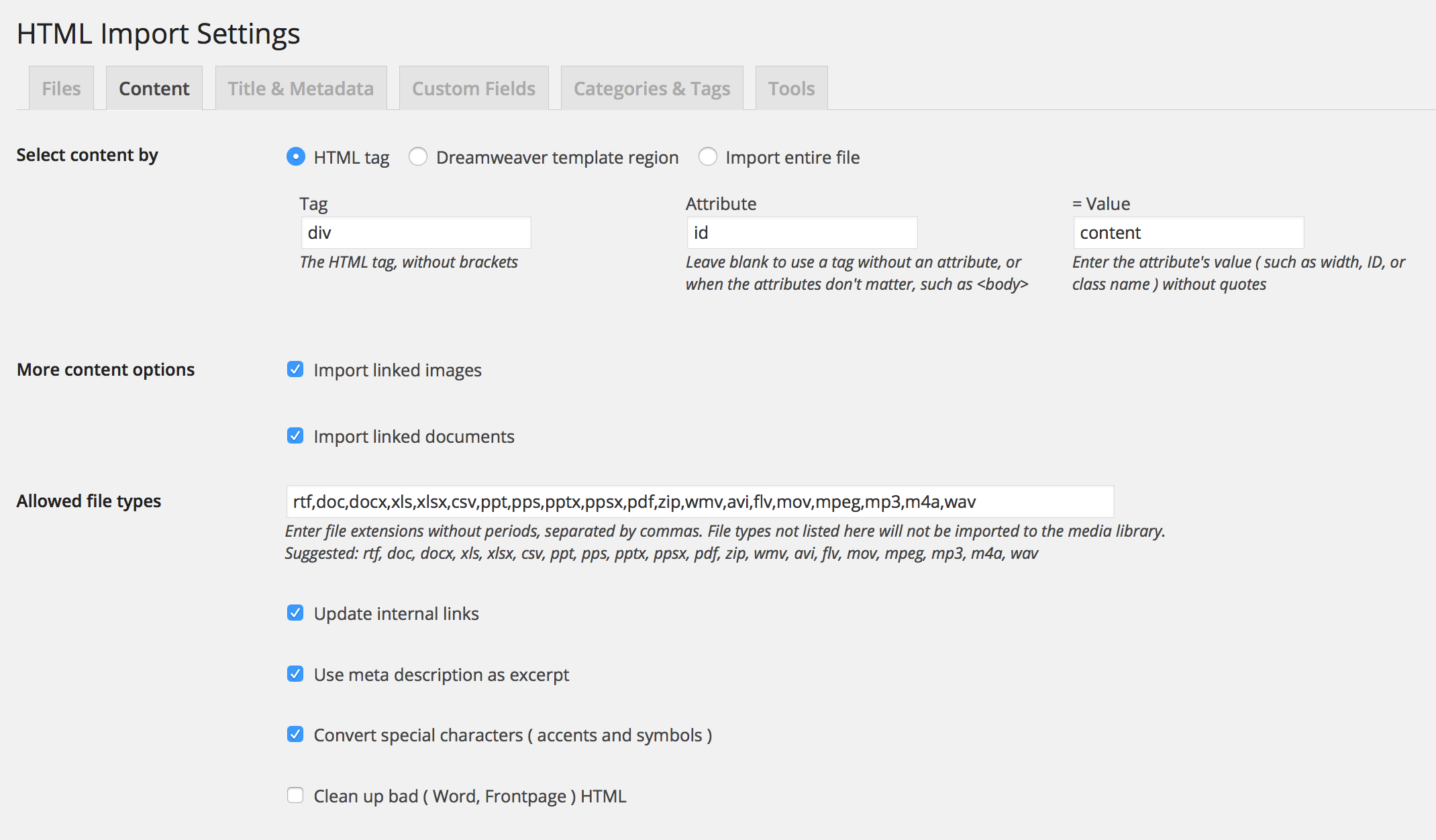
Content settings 
HTML cleanup options 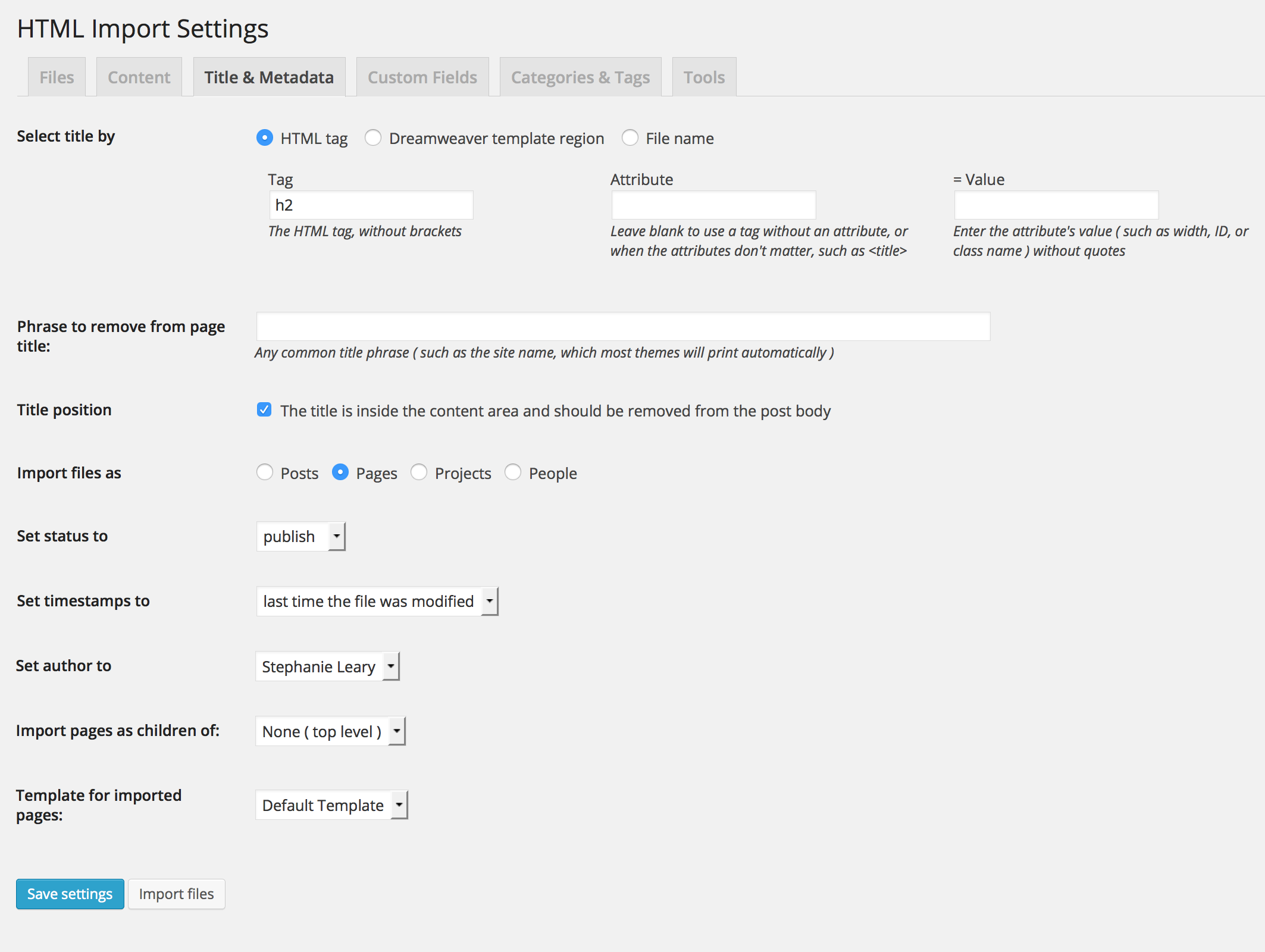
Title and metadata settings 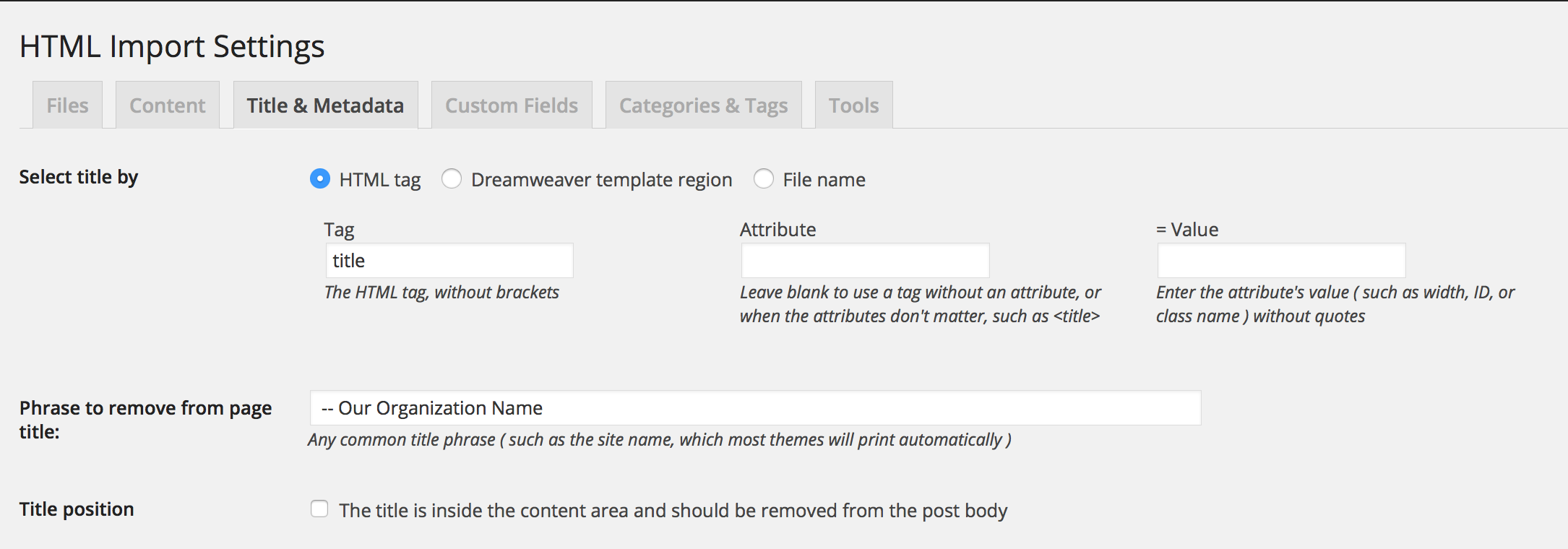
Alternative title specifications 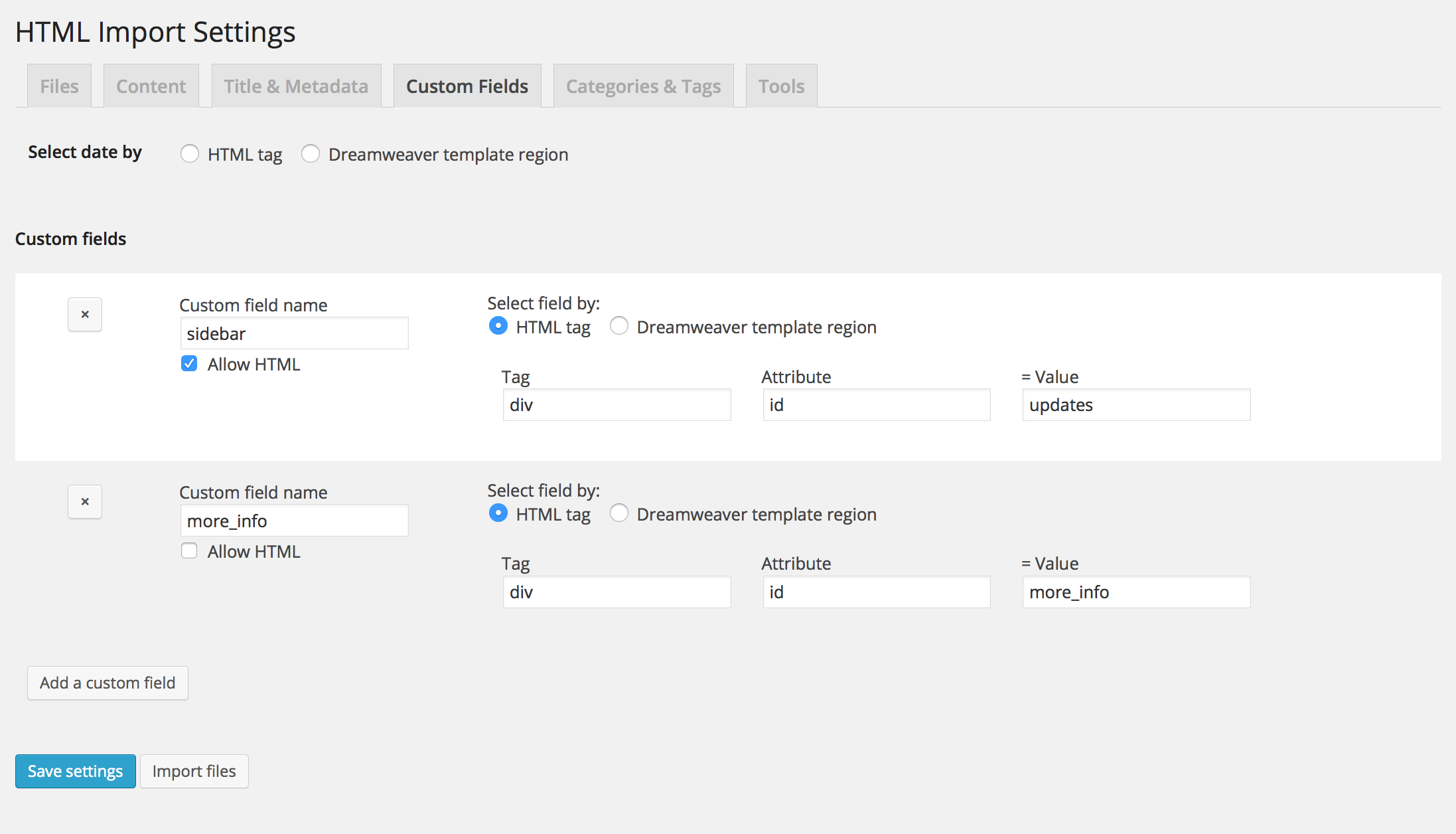
Custom field settings 
Category, tag, and taxonomy settings 
Import screen (directory/file selection) 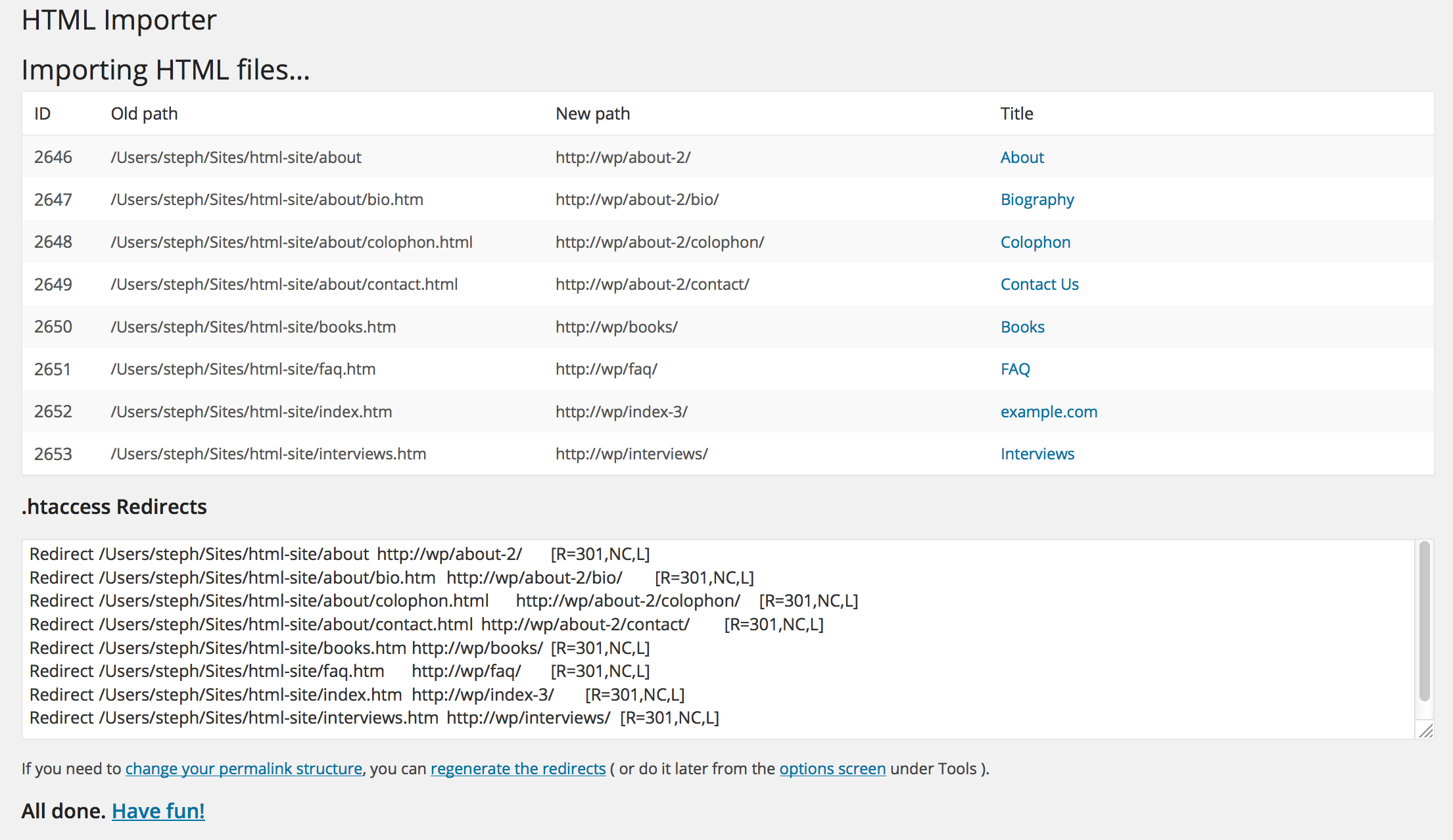
Completed import: pages, rewrite rules, and images 
Sample directory and file structure 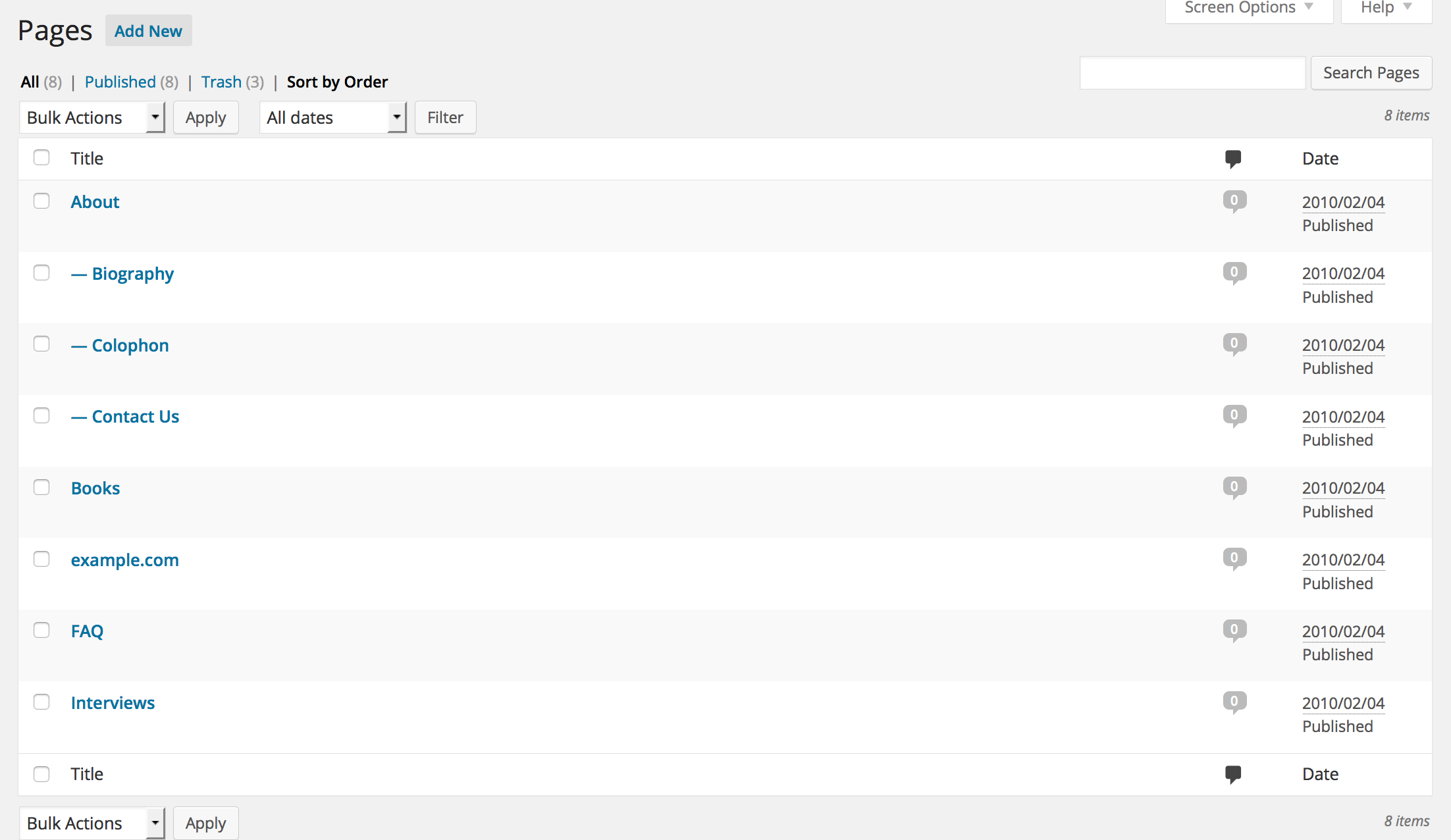
The same site, after the import (directory hierarchy preserved as parent/child pages)
Installation
- Unzip the files and upload the plugin directory to
/wp-content/plugins/ - Activate the plugin through the ‹Plugins› menu in WordPress
- Go to Settings → HTML Import to begin. You must save the settings before proceeding to Tools → Import → HTML.
FAQ
- Installation Instructions
-
- Unzip the files and upload the plugin directory to
/wp-content/plugins/ - Activate the plugin through the ‹Plugins› menu in WordPress
- Go to Settings → HTML Import to begin. You must save the settings before proceeding to Tools → Import → HTML.
- Unzip the files and upload the plugin directory to
- My title imported, but the content was empty! (Or vice versa.)
-
You didn’t find the right HTML tag that surrounds the content you wanted to import. Open up one of your old files in a browser and use its inspector (or Firebug) to select the content you want. Look for the tag that surrounds that content and find something unique about it. (An ID attribute is best, but anything unique will work. If it’s a table cell, a unique width will do just fine.) The enter the tag name, the attribute name, and the attribute’s value into the separate boxes in the Content section of the importer’s options page.
See the User Guide for details and examples.
- Does this work on Windows servers?
-
Yes! Let me know if you encounter any problems.
- Will the importer duplicate the design of my old site?
-
No. The importer simply extracts the relevant part of each HTML file and copies it into a WordPress post. You’ll need to create a custom theme if you want to preserve the site’s appearance as well as its content.
- Will this work on large numbers of HTML files?
-
Yes, it has been used to import over a thousand pages, and did so in a couple of minutes. However, you might need to adjust PHP’s
max_execution_timesetting as described below. - I import a few files and then the script times out. What can I do?
-
The importer will attempt to work around your server’s
max_execution_timesetting for PHP (usually 30 seconds), but some servers don’t allow this. You can try to increase it by adding a line to your.htaccessfile:php_value max_execution_time 160If that gets you further but still doesn’t finish, just increase the number (it’s in seconds). However, note that your host might get irritated with you for hogging the server’s resources. If you have a lot of files to import, it’s best to install WordPress on your desktop (XAMPP for Windows and MAMP for Macs make it pretty easy) and run the importer there instead of doing it on your live server.
It’s also quite possible that the script is trying to use more memory than your server allows. You can try to change that setting, too, in
.htaccess:php_value memory_limit 1024M - Should I remove ‹images› from the list of skipped directories if I want to import images?
-
The skipped directory setting just tells the importer where to look for HTML files. Linked images will be imported no matter where they’re located.
- Can I import files from another server?
-
No. The files must be on the same server as your WordPress installation. I have no intention of ever making this plugin import files from URLs. You are welcome to fork the code if you want to add this feature.
Reviews
Contributors & Developers
“HTML Import 2” is open source software. The following people have contributed to this plugin.
ContributorsTranslate “HTML Import 2” into your language.
Interested in development?
Browse the code, check out the SVN repository, or subscribe to the development log by RSS.
Changelog
2.6
- Removed ancient magic runtime quotes call, wow.
- Checking for empty string instead of empty() to allow for directories named ‹0› or similar
- Bail out earlier if XML can’t be loaded, to avoid fatal errors
- More efficient link rewriting
2.5.1
- Fixed warnings and notices related to the custom category walker.
- Fixed bug where the page parent option displayed incorrectly in sites with no published pages.
2.5
- Custom fields can now allow the same HTML tags as content
- Fixed a problem with some image paths
- Made image and link searches case-insensitive (props Clean Forest Solutions)
- Fixed some incorrectly escaped options that would trigger translations on things that shouldn’t be translated
- Page template selections are now pre-selected when returning to the options page (props Lee Fent)
2.4
- You can now specify more than one index filename (e.g. ‹index.php, default.htm›)
- New option to remove the imported title from within the content area
- Fallbacks: if your chosen tag/area is empty or does not exist, the importer will select
<body>for content and<title>for the title. As a last resort, if there is no title, the original file name will become the title. - You can now use a custom field named ‹post_tag› to import tags from a portion of the file
- UI fixes for the custom fields tab
- Bug fix: the importer now correctly recognizes absolute links to images
2.3
- New option to import an entire file’s contents instead of selecting a portion of it. (Props Shawn Zilbert.)
- New option to generate the title from the filename. (Props Shawn Zilbert.)
- New option to preserve the original filename (minus the extension) as the imported page slug. (Sponsored by NYCinsiderguide.com)
- New option to choose the date from an HTML tag or Dreamweaver region.
- New option to import custom fields.
- UI cleanup. The tabs should work a bit better.
- «asXML() on a non-object» errors should be less frequent now.
- Fixed a problem with file types that would cause blank thumbnails and images. (Props mchev2 and Carsten Bach.)
2.2
- Now imports media files other than images. Uses
rawurldecode()to remove junk like%20from file names, and thus should now handle situations where your link is something likemy%20file.docand your file is actually calledmy file.doc. - Now handles images with https srcs.
- Removed a pointless security check that was preventing people from uploading valid image files.
2.1
- New option to fix internal links. Also, the importer now bakes you cookies. (Kidding about the cookies.) (August 23, 2011)
2.0.2
- Added some helpers to work around servers that do not support PHP’s multibyte string functions. (August 12, 2011)
2.0.1
- Added option to set the page template for hierarchical post types. (August 2, 2011)
2.0
- New option to import images linked in the imported HTML files. It can handle most relative paths as well as absolute URLs. The report includes a list of the image paths that couldn’t be found.
- Now supports all public custom post types and taxonomies (including hierarchical ones).
- Completely different, much better handling of special characters.
- The import screen now lets you upload a single file.
- New user interface. The options form is now broken up into several tabbed sections. Categories and other hierarchical taxonomies are selected with checkboxes.
- The options form is now separate from the importer. It will now check your settings before the importer runs — for example, you’ll get a warning if your beginning directory isn’t readable.
- The importer itself is now based on the WordPress import class, which means it looks and works more like other importers. It is located under Tools→Import (but you should visit the settings screen first).
- Files› old URLs are now stored as custom fields in the imported posts. There’s now an option to regenerate the redirects for your imported files, which is handy if you changed your permalink structure after you finished importing.
- When importing directories as hierarchical post types (like pages), the importer now uses the default directory file (like index.html) for the parent page’s contents.
- Now skips Dreamweaver
_notesand Frontpage_vti_cnfdirectories automatically. - Now makes proper use of the Settings API for better security and data validation.
- Help screen and user guide.
- Now requires at least WP 3.0. (July 15, 2011)
1.30
- The ‹.,..› directories are no longer optional, so you can’t accidentally import hundreds of empty posts/pages by removing these from the skipped directories option.
- The beginning directory default is now based on the path to your WordPress installation. There’s also a hint shown below the field. This should help people locate their import directory correctly.
- There’s now an option to enter your old URL. If you enter it, your .htaccess redirects should work as displayed. If you leave it blank, you’ll have to doctor the paths afterward, as before.
- Character encoding is now optional. If your special characters did not import correctly before, try again with this option unchecked (which is now the default).
- Options are now deleted on plugin uninstall instead of deactivate. (Sorry about that.)
- Code cleanup in preparation for version 2.0. (June 24, 2011)
1.21
- same as 1.2; not sure why the plugin repository can’t count
1.2
- Added custom taxonomy options
- Better handling of mb encoding function and asXML
- Better security checking
- Added translation support (January 24, 2010)
1.13
- Fixed a bug in 1.11 when importing content specified by a tag (thanks, mjos)
- Added an option to assign a category or tag to all imported posts
- This is 1.12, only uncorrupted (September 13, 2009)
1.12
- Fixed a bug in 1.11 when importing content specified by a tag (thanks, mjos)
- Added an option to assign a category or tag to all imported posts (September 13, 2009)
1.11
- Left some debugging code in 1.1, oops! (August 15, 2009)
1.1
- Added Word cleanup option (August 14, 2009)
1.04
- Better user capability check (August 3, 2009)
1.03
- Still better error handling
- minor code cleanup (August 1, 2009)
1.02
- Better error handling for
fopenandfile_get_contents(July 31, 2009)
1.01
- jQuery bug fixed
- better Windows compatibility (July 31, 2009)
1.0
- First release (July 26, 2009)